A helicopter flying 3590 feet – Prepare for takeoff as we embark on a captivating journey to unravel the intricacies of a helicopter flying at the remarkable altitude of 3590 feet. This aerial odyssey will delve into the dynamics, safety considerations, and practical applications of high-altitude helicopter operations, promising an enlightening exploration for aviation enthusiasts and curious minds alike.
Soaring above the ordinary, helicopters at this altitude navigate unique challenges and offer exceptional capabilities. Join us as we dissect the factors influencing flight performance, uncover the techniques employed by skilled pilots, and examine the environmental conditions that shape these extraordinary flights.
Altitude Information
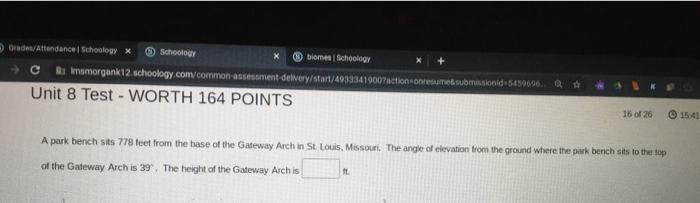
The helicopter’s altitude of 3590 feet is significant for several reasons. Helicopters typically operate at altitudes ranging from a few hundred feet to several thousand feet, depending on factors such as the mission, weather conditions, and terrain.
The altitude of 3590 feet provides the helicopter with a balance of advantages and considerations. At this altitude, the helicopter can:
Clearance from Obstacles
- Maintain a safe distance from obstacles on the ground, such as buildings, trees, and power lines.
- Allow for safe maneuvering and emergency procedures in the event of an engine failure or other malfunction.
Visibility and Situational Awareness
- Provide the pilot with a good view of the surrounding terrain, allowing for better situational awareness and navigation.
- Enhance the pilot’s ability to spot potential hazards or obstacles in the flight path.
Aerodynamic Efficiency
- Operate at an altitude where the air is less dense, reducing drag and improving fuel efficiency.
- Allow for higher speeds and longer flight times.
Weather Considerations
- Avoid areas of low visibility or adverse weather conditions, such as fog, clouds, or precipitation.
- Provide a buffer zone above potential weather hazards, such as thunderstorms or icing conditions.
Flight Dynamics

The flight dynamics of a helicopter at 3590 feet are influenced by several factors, including altitude, air density, and temperature. At this altitude, the air is less dense, which can affect the helicopter’s performance in terms of speed, maneuverability, and stability.
A helicopter hovered serenely at 3590 feet, its blades slicing through the air with a rhythmic whir. As I gazed up at this magnificent feat of engineering, my mind drifted to the complexities of history. I recalled the pivotal events and influential figures covered in the abeka world history test 10 . The lessons learned from those bygone eras echoed in the present, shaping our understanding of the world.
And as the helicopter soared effortlessly, I couldn’t help but marvel at the intricate tapestry of human history that it symbolized.
As altitude increases, the air becomes less dense. This means that there is less air resistance acting on the helicopter, which can result in a higher maximum speed. However, the reduced air density also means that the helicopter’s lift is reduced, which can make it more difficult to maintain altitude and maneuver.
Techniques for Maintaining Altitude
Pilots use a variety of techniques to maintain altitude in a helicopter, including adjusting the collective, cyclic, and rudder controls. The collective controls the helicopter’s overall lift, while the cyclic controls the helicopter’s pitch and roll. The rudder controls the helicopter’s yaw.
- Adjusting the collective:Increasing the collective increases the helicopter’s lift, which can be used to climb or maintain altitude. Decreasing the collective decreases the helicopter’s lift, which can be used to descend or slow down.
- Adjusting the cyclic:Tilting the cyclic forward causes the helicopter to pitch forward and descend. Tilting the cyclic back causes the helicopter to pitch back and climb. Tilting the cyclic left or right causes the helicopter to roll left or right.
- Adjusting the rudder:Moving the rudder left or right causes the helicopter to yaw left or right. This can be used to counteract the effects of wind or to turn the helicopter.
Environmental Conditions

Environmental conditions can significantly affect helicopter flight at high altitudes, especially at 3590 feet. Understanding these conditions and their impact is crucial for pilots to ensure safe and efficient flight operations.
Wind, A helicopter flying 3590 feet
Wind is a major environmental factor that affects helicopter flight. Strong winds can cause the helicopter to drift off course, making it difficult to maintain a stable flight path. Wind shear, a sudden change in wind speed or direction, can also be hazardous, especially at high altitudes where the helicopter is more susceptible to wind gusts.
Temperature
Temperature plays a significant role in helicopter performance. High temperatures can reduce the helicopter’s lift and increase drag, affecting its ability to climb and maneuver. Conversely, low temperatures can increase lift and reduce drag, making the helicopter more responsive and agile.
Visibility
Visibility is another important environmental condition that affects helicopter flight. Poor visibility, such as fog, haze, or smoke, can make it difficult for the pilot to see and navigate, increasing the risk of collisions and other accidents.
Safety Considerations
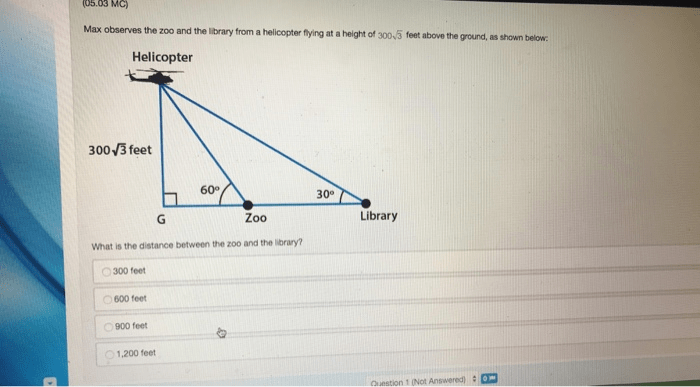
Flying a helicopter at 3590 feet poses unique safety considerations due to the high altitude. Understanding these risks and adhering to safety protocols is crucial for ensuring the well-being of passengers and crew.
At high altitudes, the air becomes thinner, leading to reduced oxygen levels. This can result in hypoxia, a condition where the body’s tissues do not receive enough oxygen. Symptoms of hypoxia include impaired judgment, disorientation, and loss of consciousness.
Safety Protocols
To mitigate these risks, pilots must follow strict safety protocols when flying at high altitudes. These include:
- Supplemental Oxygen:Pilots and passengers must use supplemental oxygen systems to maintain adequate oxygen levels.
- Altitude Acclimatization:Pilots should allow sufficient time for their bodies to acclimatize to the high altitude before flying.
- Flight Planning:Careful flight planning is essential to avoid flying in areas with low oxygen levels or unfavorable weather conditions.
- Emergency Procedures:Pilots must be trained in emergency procedures for dealing with hypoxia and other high-altitude hazards.
Applications and Use Cases
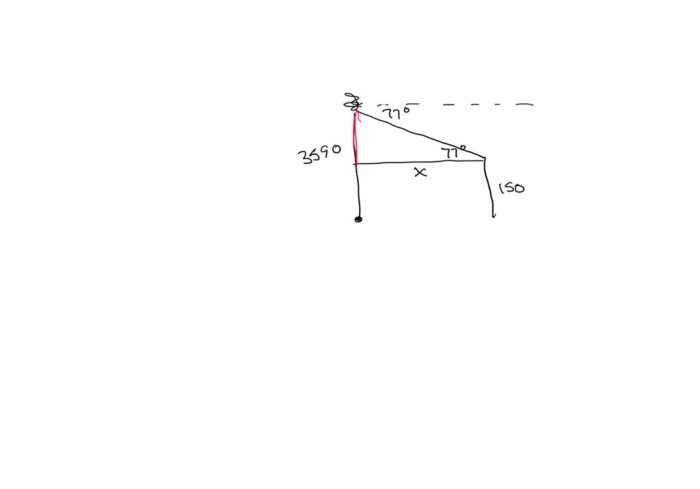
Helicopters are used in various applications and use cases at an altitude of 3590 feet, offering unique advantages in high-altitude operations.
One common application is mountain rescue, where helicopters can quickly reach and evacuate injured hikers or climbers from remote and inaccessible areas.
Aerial Photography and Mapping
- Helicopters provide a stable and maneuverable platform for aerial photography and mapping, allowing for high-resolution images and accurate data collection from high altitudes.
- They can capture aerial imagery for urban planning, land use analysis, and disaster response.
Search and Rescue
- Helicopters are invaluable in search and rescue operations, particularly in mountainous or remote areas.
- Their ability to hover and maneuver in confined spaces makes them ideal for locating and extracting survivors.
Power Line Inspection
- Helicopters are used for power line inspection, providing a safe and efficient way to monitor the condition of power lines from above.
- They can quickly identify potential issues, such as damaged insulators or vegetation encroachment, ensuring reliable power transmission.
FAQ Overview: A Helicopter Flying 3590 Feet
What factors influence the altitude at which a helicopter flies?
Altitude selection is influenced by mission objectives, weather conditions, terrain, air traffic, and the helicopter’s performance capabilities.
How do pilots maintain altitude in a helicopter?
Pilots utilize a combination of flight controls, including the collective, cyclic, and rudder, to adjust the helicopter’s lift, pitch, and direction, enabling precise altitude maintenance.
What safety considerations are crucial for high-altitude helicopter operations?
Safety protocols include thorough pre-flight planning, adherence to altitude restrictions, proper oxygen equipment, and emergency procedures for potential altitude-related issues.
