Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of geometry with Big Ideas Math Geometry Chapter 10 Answers. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental principles of geometric shapes, their properties, and their practical applications in the real world. Through engaging explanations and step-by-step solutions, this resource empowers learners to grasp geometric concepts with clarity and confidence.
Delving into the intricacies of geometric shapes, this chapter explores the characteristics and properties of triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and more. It elucidates the significance of angles, sides, and symmetry in defining these shapes and provides real-world examples to illustrate their prevalence in everyday objects and structures.
Chapter Overview
Chapter 10 of Big Ideas Math Geometry introduces the fundamental concepts of geometric shapes and their properties. It explores the significance of geometric shapes in real-world applications, providing a solid foundation for understanding geometry and its practical implications.
Geometric Shapes
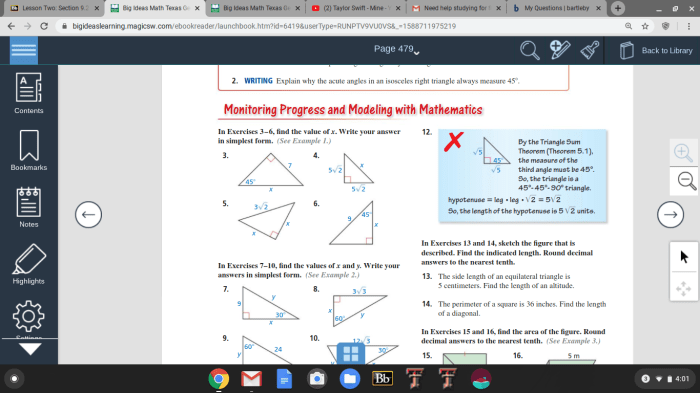
Geometric shapes are defined as closed figures with specific properties. In this chapter, we will explore different types of geometric shapes, including triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles. We will discuss their properties, such as angles, sides, and symmetry, and provide examples of how these shapes are used in everyday objects and structures.
Triangles
- A triangle is a three-sided polygon with three angles and three vertices.
- Triangles can be classified based on their side lengths (equilateral, isosceles, scalene) and their angle measures (acute, right, obtuse).
- The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
Quadrilaterals
- A quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon with four angles and four vertices.
- Quadrilaterals can be classified based on their side lengths and angle measures (e.g., square, rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid).
- The sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is always 360 degrees.
Circles
- A circle is a closed curve that lies in a plane and has a fixed distance from a given point called the center.
- Circles are characterized by their radius and diameter, which are related by the formula d = 2r.
- The circumference of a circle is given by the formula C = 2πr, and its area is given by the formula A = πr².
Measurement and Properties

Measuring and calculating the area, perimeter, and volume of geometric shapes are essential skills in geometry. In this chapter, we will explore the formulas and step-by-step processes for performing these calculations.
Area
- The area of a shape represents the amount of surface it covers.
- Formulas for calculating the area of different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles, will be provided.
- The units of area are square units (e.g., square centimeters, square meters).
Perimeter
- The perimeter of a shape represents the distance around its boundary.
- Formulas for calculating the perimeter of different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles, will be provided.
- The units of perimeter are linear units (e.g., centimeters, meters).
Volume
- The volume of a shape represents the amount of space it occupies.
- Formulas for calculating the volume of different shapes, such as cubes, prisms, and cylinders, will be provided.
- The units of volume are cubic units (e.g., cubic centimeters, cubic meters).
Transformations: Big Ideas Math Geometry Chapter 10 Answers

Geometric transformations involve moving or changing the position or size of a shape without altering its shape. In this chapter, we will explore different types of transformations, including translations, rotations, and reflections.
Translations
- A translation is a transformation that moves a shape from one point to another without changing its size or orientation.
- Translations are described using vectors, which specify the direction and distance of the movement.
Rotations
- A rotation is a transformation that turns a shape around a fixed point by a specified angle.
- Rotations are described using the angle of rotation and the center of rotation.
Reflections
- A reflection is a transformation that flips a shape over a line called the line of reflection.
- Reflections are described using the equation of the line of reflection.
Coordinate Geometry
Coordinate geometry introduces the concept of representing geometric shapes on a coordinate plane. In this chapter, we will learn how to plot points, graph geometric shapes, and explore the relationship between geometric shapes and their equations.
Coordinate Plane
- The coordinate plane is a two-dimensional plane with two perpendicular axes, the x-axis and the y-axis.
- Points on the coordinate plane are represented by ordered pairs (x, y).
Plotting Points
- To plot a point on the coordinate plane, locate its x-coordinate on the x-axis and its y-coordinate on the y-axis.
- The point is then located at the intersection of the two lines.
Graphing Geometric Shapes
- Geometric shapes can be graphed on the coordinate plane by plotting their vertices and connecting them with line segments.
- The equation of a geometric shape can be used to graph it on the coordinate plane.
Applications in Real-World Problems
Geometric concepts are widely applied in various fields, including architecture, engineering, art, and everyday life. In this chapter, we will explore real-world examples of how geometric concepts are used to solve problems and create innovative solutions.
Architecture, Big ideas math geometry chapter 10 answers
- Geometric shapes are used in the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- For example, triangles are used to create strong and stable structures, while circles are used to create smooth and flowing designs.
Engineering
- Geometric shapes are used in the design of machines, vehicles, and other products.
- For example, circles are used in gears to transmit motion, while triangles are used in bridges to support weight.
Art
- Geometric shapes are used in art to create patterns, textures, and compositions.
- For example, triangles are used in abstract art to create dynamic and visually appealing designs.
Everyday Life
- Geometric shapes are used in everyday objects, such as furniture, clothing, and packaging.
- For example, circles are used in wheels to provide smooth movement, while squares are used in boxes to provide stability.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of geometric shapes in real-world applications?
Geometric shapes play a crucial role in various fields, including architecture, engineering, art, and everyday life. They provide the foundation for designing and constructing buildings, bridges, and other structures, ensuring stability and functionality. Geometric principles are also essential in creating aesthetically pleasing designs in art and graphic design.
How can I improve my understanding of geometric transformations?
Practice is key to mastering geometric transformations. Regularly work through examples and apply the concepts to different shapes. Visualize the transformations and their effects on the original shape. Additionally, seek guidance from your teacher or a tutor if needed.