In a competitive market positive npv projects are – In a competitive market, positive net present value (NPV) projects are essential for businesses to succeed and thrive. NPV is a financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment project, and it represents the difference between the present value of the project’s cash inflows and outflows over its lifetime.
Positive NPV projects are those that have a positive NPV, indicating that the project is expected to generate a return on investment that exceeds the initial investment cost.
Identifying and executing positive NPV projects in a competitive market can be challenging, but it is crucial for businesses to remain competitive and profitable. This article will explore the characteristics of a competitive market, the significance of NPV in investment decisions, and strategies for identifying and evaluating positive NPV projects in such an environment.
Competitive Market Dynamics
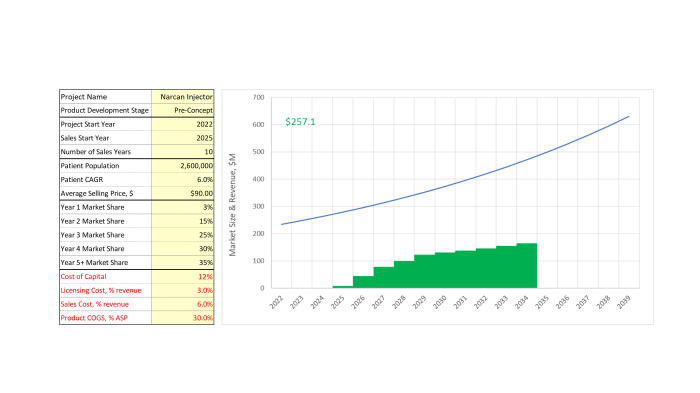
In a competitive market, numerous businesses compete for a share of the same customer base. This intense rivalry can significantly impact businesses, influencing their strategies, pricing, and overall performance.
The interplay between supply and demand plays a crucial role in determining market competitiveness. When supply exceeds demand, competition intensifies, leading to lower prices, increased product differentiation, and reduced profit margins. Conversely, when demand outstrips supply, businesses have more bargaining power, enabling them to charge higher prices and earn higher profits.
Industries with high levels of competition include technology, retail, and food and beverage. In these markets, businesses constantly innovate and differentiate their products to attract customers and gain market share.
In contrast, industries with low levels of competition, such as utilities and healthcare, are characterized by high barriers to entry, government regulations, and limited product differentiation.
Positive Net Present Value (NPV) Projects
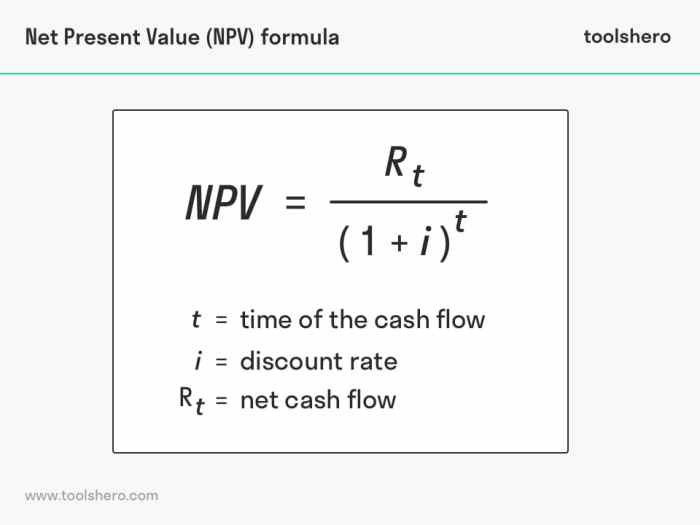
Net Present Value (NPV) is a financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment project. It represents the present value of all future cash flows generated by the project, discounted back to the present using an appropriate discount rate.
A positive NPV indicates that the project is expected to generate a return greater than the cost of capital, making it a potentially attractive investment. The formula for calculating NPV is:
NPV =
Initial Investment + Σ (Cash Flowt/ (1 + Discount Rate) t)
where:
- Initial Investment: The initial cost of the project
- Cash Flow t: The cash flow generated by the project in period t
- Discount Rate: The rate used to discount future cash flows back to the present
Factors that influence NPV include the size and timing of cash flows, the project’s lifespan, and the discount rate used.
Identifying Positive NPV Projects in a Competitive Market
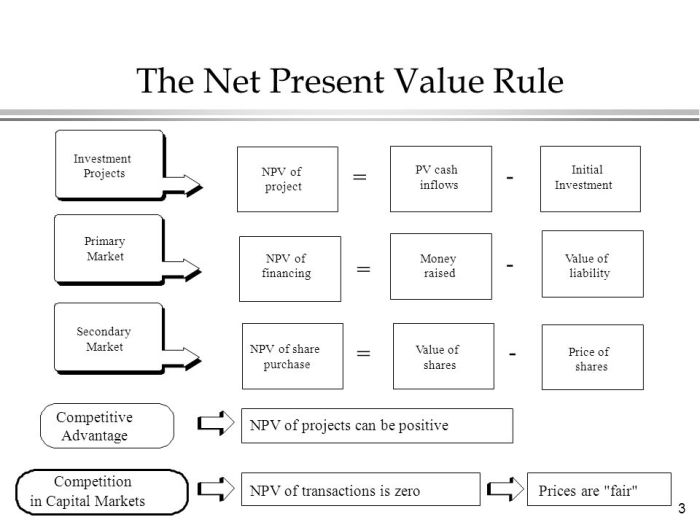
Identifying positive NPV projects in a competitive market can be challenging. Market research and industry analysis are essential tools for uncovering potential opportunities.
Market research provides insights into customer needs, preferences, and competitive dynamics. This information can help businesses identify gaps in the market and develop products or services that meet unmet demand.
Industry analysis involves studying the competitive landscape, industry trends, and potential threats. By understanding the competitive environment, businesses can better position themselves to identify and exploit opportunities for positive NPV projects.
Competitive Advantages and NPV: In A Competitive Market Positive Npv Projects Are
Competitive advantages can significantly contribute to positive NPV projects. Businesses with strong competitive advantages can command higher prices, reduce costs, and differentiate their products or services, leading to increased profitability.
Innovation, differentiation, and cost leadership are three key strategies for creating competitive advantages. Innovation involves developing new products or processes that meet unmet customer needs. Differentiation involves creating unique products or services that stand out from the competition. Cost leadership involves achieving lower production or operating costs than competitors.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Risk assessment is crucial in evaluating NPV projects in a competitive market. Risks can arise from various sources, including market fluctuations, technological changes, and competitive threats.
Types of risks associated with investment projects include market risk, operational risk, and financial risk. Market risk refers to the potential for losses due to changes in market conditions. Operational risk refers to the potential for losses due to disruptions in the project’s operations.
Financial risk refers to the potential for losses due to changes in interest rates or currency exchange rates.
Strategies for managing risk include diversification, hedging, and insurance. Diversification involves investing in a variety of assets to reduce the overall risk of the portfolio. Hedging involves using financial instruments to offset potential losses. Insurance provides protection against specific risks.
User Queries
What is a competitive market?
A competitive market is one in which there are many buyers and sellers, and no single entity has a dominant market share. This results in intense competition, which can drive down prices and increase innovation.
What is NPV?
NPV is a financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment project. It represents the difference between the present value of the project’s cash inflows and outflows over its lifetime.
How can I identify positive NPV projects in a competitive market?
Identifying positive NPV projects in a competitive market requires thorough market research and industry analysis. Businesses should look for projects that have a competitive advantage, such as innovation, differentiation, or cost leadership.