Embark on a scientific expedition with Experiment 23 Determination Equilibrium Constant Answers, a comprehensive resource that unravels the intricacies of chemical reactions and equilibrium. Delve into the significance of equilibrium constants, explore experimental procedures, and uncover the practical applications of this fundamental concept in diverse scientific fields.
As we delve into the heart of Experiment 23, we will meticulously examine the experimental setup, data collection techniques, and analytical methods employed to determine equilibrium constants accurately. Furthermore, we will scrutinize potential sources of error and explore strategies to minimize their impact on the reliability of our results.
1. Overview of Experiment 23
Determination of Equilibrium Constant
Experiment 23 aims to determine the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction by measuring the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium. Equilibrium constant is a measure of the extent to which a reaction proceeds towards completion and is essential for predicting the behavior of chemical systems.
The equilibrium constant is represented by the symbol K and is calculated as the ratio of the concentrations of products to the concentrations of reactants at equilibrium, each raised to their stoichiometric coefficients. Understanding equilibrium constants is crucial for various applications in chemistry, including predicting reaction outcomes, designing chemical processes, and studying the behavior of complex systems.
2. Experimental Setup and Procedures
Materials and Equipment
- Reactants and products of the chemical reaction under study
- Analytical balance
- Spectrophotometer or other analytical instrument for measuring concentrations
- Cuvettes or other containers for reaction mixtures
- Constant-temperature bath or incubator
- Safety goggles, gloves, and lab coat
Procedures, Experiment 23 determination equilibrium constant answers
- Prepare a series of reaction mixtures with varying initial concentrations of reactants.
- Allow the mixtures to reach equilibrium by incubating them at a constant temperature for a sufficient amount of time.
- Measure the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium using the appropriate analytical technique.
- Calculate the equilibrium constant K using the measured concentrations and the stoichiometry of the reaction.
- Repeat the experiment at different temperatures to determine the temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant.
Safety Precautions
- Wear appropriate safety gear, including goggles, gloves, and a lab coat.
- Handle chemicals with care, following proper laboratory safety protocols.
- Dispose of waste chemicals and materials according to established procedures.
3. Data Collection and Analysis
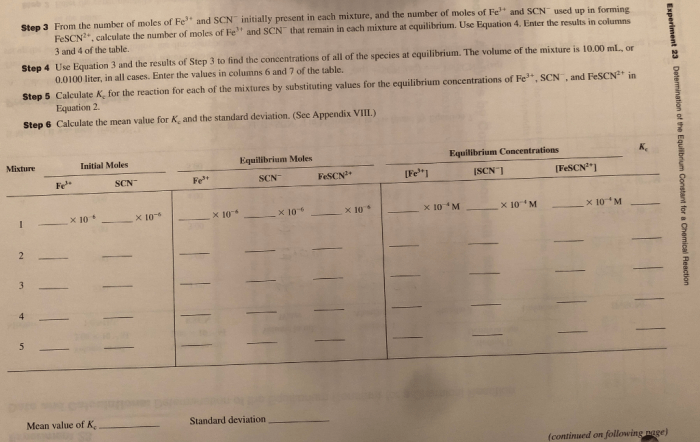
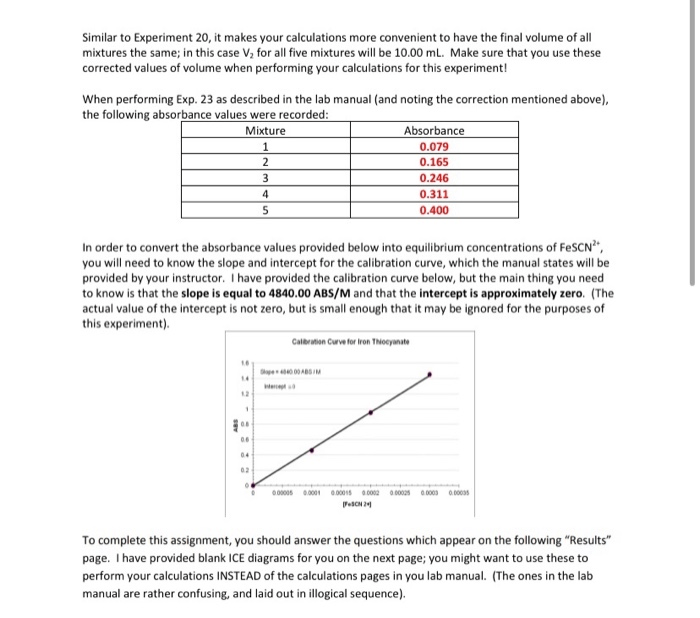
During Experiment 23, data is collected by measuring the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium. Spectrophotometry is a common technique used for this purpose, where the absorbance of light at specific wavelengths is measured to determine the concentrations of the species of interest.
The equilibrium constant K is calculated using the following equation:
K = [products]^m / [reactants]^n
where m and n are the stoichiometric coefficients of the products and reactants, respectively, and [ ] denotes the molar concentrations at equilibrium.
4. Sources of Error
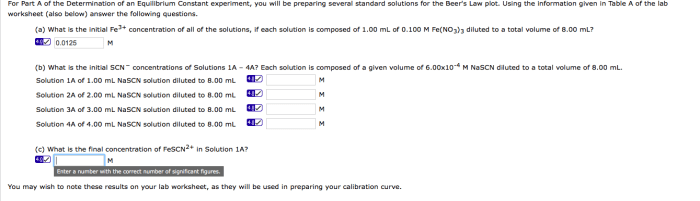
Several sources of error can affect the accuracy of the equilibrium constant determination, including:
- Measurement errors in the concentrations of reactants and products
- Incomplete equilibration of the reaction
- Side reactions or competing reactions
- Temperature fluctuations
To minimize these errors, careful experimental techniques and data analysis methods are essential. Multiple measurements and statistical analysis can help reduce the impact of random errors. Ensuring complete equilibration and controlling for side reactions are crucial for obtaining accurate results.
5. Applications of Equilibrium Constant: Experiment 23 Determination Equilibrium Constant Answers
The equilibrium constant is a valuable tool in various fields of science and engineering, including:
- Predicting the direction and extent of chemical reactions
- Designing chemical processes for optimal yield and efficiency
- Studying the behavior of complex systems, such as biochemical pathways and environmental processes
- Determining the solubility and partitioning of compounds in different phases
By understanding the equilibrium constant, scientists and engineers can gain insights into the behavior of chemical systems and optimize processes accordingly.
Popular Questions
What is the significance of equilibrium constants in chemical reactions?
Equilibrium constants provide valuable insights into the extent and direction of chemical reactions, allowing us to predict the behavior of reactants and products under varying conditions.
How can we minimize the impact of errors in equilibrium constant determination?
Rigorous adherence to experimental procedures, careful calibration of equipment, and appropriate data analysis techniques can significantly reduce the influence of errors on the accuracy of equilibrium constant determination.
What are some practical applications of equilibrium constants in scientific fields?
Equilibrium constants find widespread application in chemistry, biology, and environmental science, enabling researchers to optimize reaction conditions, predict product yields, and assess the stability of complex systems.