Human evolution – skull analysis gizmo assessment answers – Embark on an enlightening journey into human evolution through the lens of skull analysis. This comprehensive guide delves into the intriguing changes observed in the human skull over time, providing a deeper understanding of our evolutionary trajectory. Prepare to uncover the fascinating relationship between skull morphology, brain evolution, and dietary adaptations.
Skull Morphology and Evolution
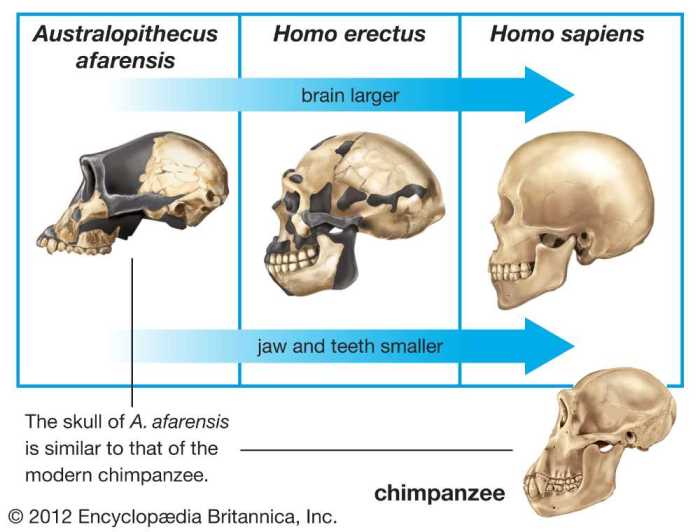
The human skull has undergone significant morphological changes throughout evolution, reflecting adaptations to changing environments and dietary habits. Early hominid skulls, such as those of Australopithecus afarensis, were characterized by a small cranial capacity, prominent brow ridges, and a prognathic jaw.
As humans evolved, the cranial capacity increased, the brow ridges became less pronounced, and the jaw became more orthognathic.
The table below compares the skull characteristics of different hominid species:
| Species | Cranial Capacity (cc) | Brow Ridges | Jaw |
|---|---|---|---|
| Homo habilis | 600-750 | Prominent | Prognathic |
| Homo erectus | 800-1200 | Less prominent | Orthognathic |
| Homo sapiens | 1300-1700 | Absent | Orthognathic |
Cranial Capacity and Brain Evolution

Cranial capacity, a measure of the volume of the braincase, has increased significantly over the course of human evolution. This increase reflects the expansion and complexity of the human brain, which has enabled humans to develop advanced cognitive abilities, such as language, tool use, and social organization.
Factors that have contributed to the increase in cranial capacity include:
- Selection for larger brains due to their adaptive advantages
- Changes in diet and lifestyle that allowed for increased brain growth
- Genetic mutations that influenced brain development
Facial Features and Diet
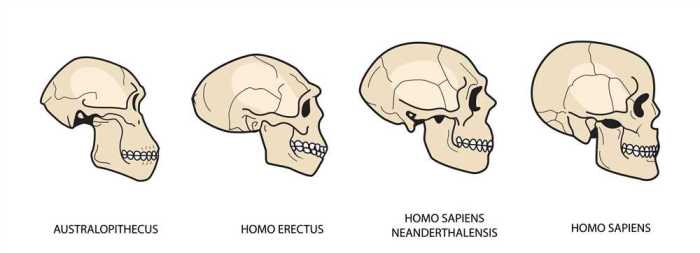
Human facial features have also undergone evolutionary changes in response to dietary adaptations. The shape of the jaws, teeth, and nasal passages has changed in relation to the shift from a primarily vegetarian diet to a more omnivorous diet.
For example, early hominids had large jaws and robust teeth adapted for chewing tough plant material. As humans began to consume more meat, the jaws became smaller and the teeth became less robust.
The infographic below illustrates the facial adaptations associated with different hominid diets:
Dental Evolution and Tool Use
The evolution of human teeth has been closely linked to tool use and food processing. The size, shape, and arrangement of teeth have changed over time in relation to the development of tools.
Early hominids had large, flat molars for grinding plant material. As humans began to use tools for cutting and preparing food, the molars became smaller and the incisors became more prominent.
Advantages of different dental adaptations for tool use and food processing include:
- Larger molars for grinding tough plant material
- Smaller molars and more prominent incisors for cutting and preparing food
- Thicker enamel for increased durability
Disadvantages of different dental adaptations for tool use and food processing include:
- Increased risk of dental damage from using teeth as tools
- Reduced efficiency in grinding plant material with smaller molars
- Increased risk of tooth decay with thinner enamel
Skull Analysis Gizmo Assessment Answers: Human Evolution – Skull Analysis Gizmo Assessment Answers
Question 1: What is the cranial capacity of the Homo habilis skull?
Answer: 600-750 cc
Question 2: Which hominid species has the most prominent brow ridges?
Answer: Homo habilis
Question 3: What is the difference between a prognathic and an orthognathic jaw?
Answer: A prognathic jaw protrudes forward, while an orthognathic jaw is aligned vertically.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of cranial capacity in human evolution?
Cranial capacity serves as an indicator of brain size, which has undergone significant expansion over the course of human evolution. This increase in brain volume reflects the growing complexity of cognitive functions, language abilities, and problem-solving skills.
How have human facial features evolved in relation to diet?
Dietary adaptations have played a pivotal role in shaping human facial features. For instance, the reduction in jaw size and the development of smaller teeth are associated with a shift towards a more omnivorous diet, while herbivorous primates tend to have larger jaws and grinding teeth.
What is the connection between dental evolution and tool use?
The evolution of human teeth is closely intertwined with the development of tool use. The smaller teeth and reduced jaw size in modern humans have allowed for greater dexterity in manipulating tools and processing food.