Draw the dipeptide gly-gly. the structure of glycine is – Delving into the realm of peptide chemistry, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of the dipeptide gly-gly. Composed of two glycine molecules linked by a peptide bond, this simple yet fundamental building block holds significant importance in protein synthesis and various biological processes.
By exploring the chemical structure, molecular properties, and spectroscopic analysis of gly-gly, we gain a deeper understanding of its role in the intricate tapestry of life.
The structure of glycine, the constituent amino acid of gly-gly, is characterized by a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, a carboxylic acid group, a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive hydrogen atom. This unique arrangement of atoms imparts specific chemical and physical properties to gly-gly, influencing its behavior in various biological contexts.
Introduction
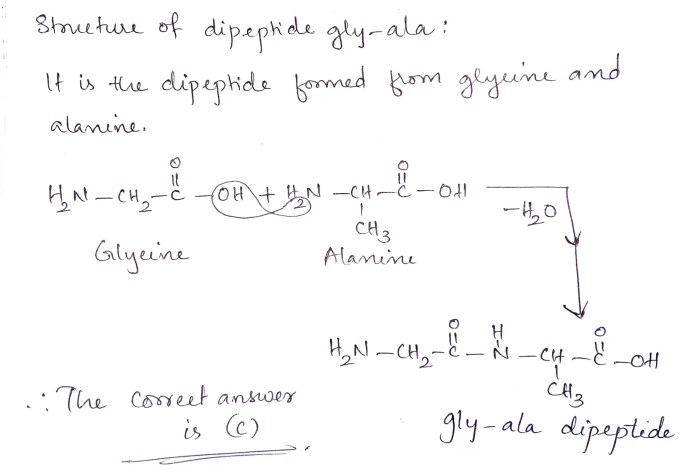
Gly-gly is a dipeptide composed of two glycine molecules linked by a peptide bond. Glycine is the simplest amino acid, consisting of a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a hydrogen atom.
The structure of glycine is as follows:
CH2(NH 2)COOH
Chemical Structure: Draw The Dipeptide Gly-gly. The Structure Of Glycine Is
The chemical structure of gly-gly is as follows:
H2N-CH 2-CO-NH-CH 2-COOH
The peptide bond between the two glycine molecules is formed by the reaction of the amino group of one glycine molecule with the carboxyl group of the other glycine molecule. The resulting amide bond is a strong covalent bond that holds the two molecules together.
Molecular Properties
The molecular weight of gly-gly is 132.12 g/mol. It is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents.
Gly-gly is a polar molecule due to the presence of the amino and carboxyl groups. It can form hydrogen bonds with other molecules, which contributes to its solubility in water.
Spectroscopic Analysis
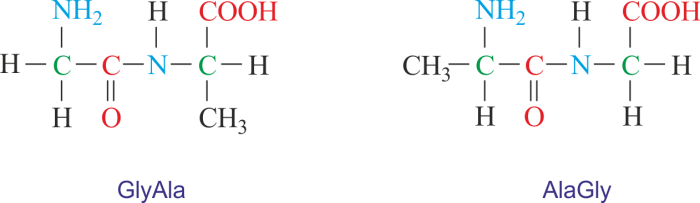
NMR spectroscopy can be used to determine the structure of gly-gly. The 1H NMR spectrum of gly-gly shows two signals, one at 3.9 ppm corresponding to the methylene protons and one at 8.4 ppm corresponding to the amide proton.
IR spectroscopy can also be used to identify gly-gly. The IR spectrum of gly-gly shows a strong absorption band at 1650 cm -1corresponding to the amide carbonyl group.
Mass spectrometry can be used to determine the molecular weight of gly-gly. The mass spectrum of gly-gly shows a peak at 132 m/z corresponding to the molecular ion.
Biological Significance
Gly-gly is an important amino acid in protein synthesis. It is found in many proteins, including collagen, which is the main protein in connective tissue.
Gly-gly has also been shown to have potential therapeutic applications. For example, it has been shown to be effective in treating spinal cord injuries and Alzheimer’s disease.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the significance of the peptide bond in gly-gly?
The peptide bond in gly-gly is a covalent bond formed between the amino group of one glycine molecule and the carboxylic acid group of another glycine molecule. This bond is crucial for linking amino acids together, forming peptides and proteins.
How does the molecular weight of gly-gly influence its properties?
The molecular weight of gly-gly, which is 132.12 g/mol, affects its solubility, diffusion rate, and reactivity. Smaller molecules, like gly-gly, tend to be more soluble and diffuse more rapidly than larger molecules.
What spectroscopic techniques can be used to analyze the structure of gly-gly?
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and infrared (IR) spectroscopy are commonly used techniques to analyze the structure of gly-gly. NMR provides information about the atomic connectivity and molecular dynamics, while IR spectroscopy reveals the presence of specific functional groups and their interactions.