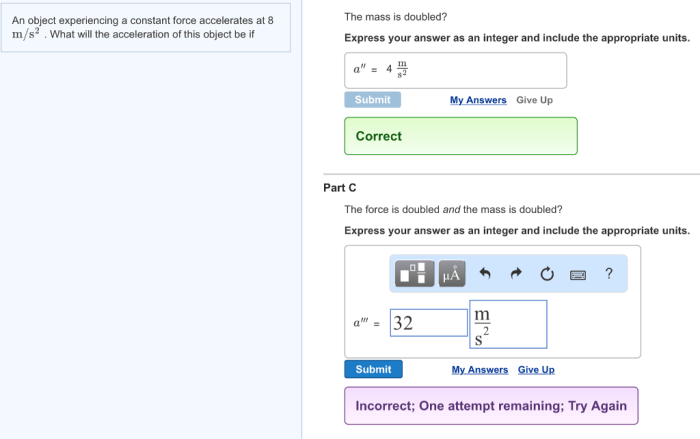
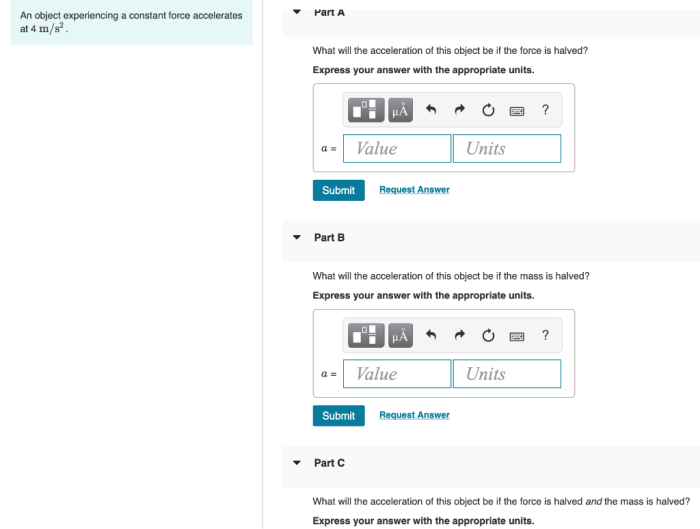
An object experiencing a constant force accelerates at 10 m/s2. This means that its velocity increases by 10 meters per second every second. This is a fundamental concept in physics that has applications in many fields, such as engineering, physics, and sports.
The equations of motion for an object experiencing a constant force are:
- v = u + at
- s = ut + 1/2 at^2
- v^2 = u^2 + 2as
where:
- v is the final velocity
- u is the initial velocity
- a is the acceleration
- t is the time
- s is the displacement
An Object Experiencing a Constant Force Accelerates at 10 m/s2
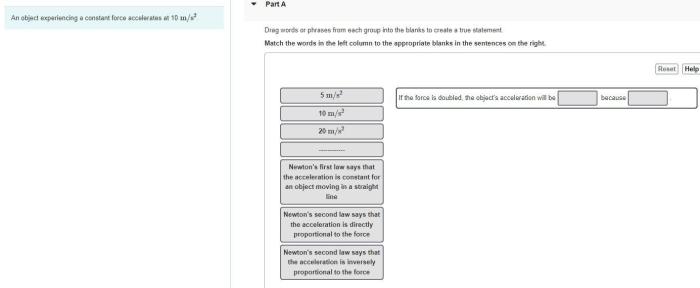
When an object is subjected to a constant force, it experiences a constant acceleration. The relationship between force, mass, and acceleration is described by Newton’s second law of motion: F = ma, where F is the force applied, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration produced.
An example of an object experiencing a constant force is a car moving at a constant speed on a level road. The force acting on the car is the friction between the tires and the road, which is constant. As a result, the car accelerates at a constant rate.
Equations of Motion
The equations of motion for an object experiencing a constant force are:
- v = u + at
- s = ut + 1/2 at 2
- v 2= u 2+ 2as
where:
- v is the final velocity
- u is the initial velocity
- a is the acceleration
- t is the time
- s is the distance traveled
These equations can be used to solve problems involving objects experiencing a constant force.
Applications, An object experiencing a constant force accelerates at 10 m/s2
The equations of motion are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Engineering: The equations of motion are used to design and analyze structures and machines.
- Physics: The equations of motion are used to study the motion of objects in the universe.
- Sports: The equations of motion are used to analyze the performance of athletes.
Understanding the equations of motion can help us to understand and predict the motion of objects in our everyday lives.
Limitations
The equations of motion are only valid for objects experiencing a constant force. If the force is not constant, the equations will not be accurate.
Additionally, the equations of motion assume that the object is moving in a straight line. If the object is moving in a curved path, the equations will not be accurate.
Frequently Asked Questions: An Object Experiencing A Constant Force Accelerates At 10 M/s2
What is the acceleration of an object experiencing a constant force?
The acceleration of an object experiencing a constant force is equal to the force divided by the mass of the object.
What are the equations of motion for an object experiencing a constant force?
The equations of motion for an object experiencing a constant force are:
- v = u + at
- s = ut + 1/2 at^2
- v^2 = u^2 + 2as
How can the equations of motion be used to solve problems?
The equations of motion can be used to solve a variety of problems, such as finding the velocity of an object after a certain amount of time, or the distance traveled by an object in a certain amount of time.