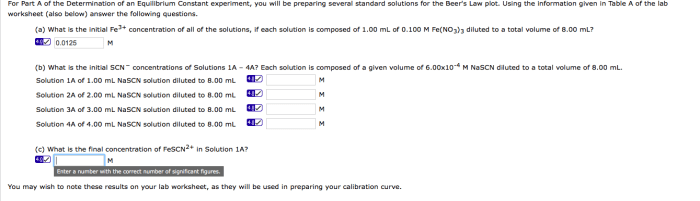
Name the compounds. Spelling counts – this adage holds immense significance in the realm of chemistry. Accurate spelling in chemical nomenclature is paramount for effective communication and understanding, ensuring the precise identification and comprehension of chemical substances.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of chemical nomenclature, exploring the rules and conventions governing the naming of inorganic and organic compounds. Through a blend of examples and practical applications, we elucidate the importance of correct spelling in facilitating seamless communication among chemists and fostering a deeper understanding of chemical concepts.
Name the Compounds

In chemistry, compounds are substances composed of two or more elements chemically bonded together. The chemical names of compounds provide important information about their composition and structure.
Chemical Names
- NaCl: Sodium chloride
- H2O: Water
- CH4: Methane
- NH3: Ammonia
- CO2: Carbon dioxide
Spelling and Nomenclature

In chemical nomenclature, correct spelling is crucial for accurate communication and understanding among scientists. Misspellings can lead to confusion and errors, as different compounds may have similar names but distinct structures and properties.
The rules and conventions for naming inorganic and organic compounds are well-established and standardized by international organizations such as the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). These rules provide a systematic approach to naming compounds based on their structure, composition, and chemical properties.
Inorganic Compounds
Inorganic compounds are typically named based on their elemental composition and oxidation states. The following rules apply:
- The name of the cation (positive ion) is written first, followed by the name of the anion (negative ion).
- The oxidation state of the metal ion is indicated using Roman numerals in parentheses after the metal name.
- For polyatomic anions, the suffix “-ide” is used, while for oxyanions, the suffix “-ate” or “-ite” is used.
Organic Compounds
Organic compounds are named based on their structure and functional groups. The following rules apply:
- The base name of the compound is derived from the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain.
- Suffixes are added to the base name to indicate the presence of functional groups, such as “-ane” for alkanes, “-ene” for alkenes, and “-ol” for alcohols.
- Prefixes are used to indicate the number and position of substituents on the parent chain.
By adhering to these rules and conventions, chemists can ensure the accurate and consistent naming of chemical compounds, facilitating clear communication and avoiding potential misunderstandings.
Examples and Applications
Accurate naming of compounds is essential for effective communication and understanding in chemistry. Correctly named compounds allow chemists to convey the exact chemical structure and properties of a substance, facilitating clear and precise discussions, research collaborations, and safety protocols.
By utilizing the principles of chemical nomenclature, chemists can assign systematic names to compounds that accurately reflect their molecular composition and structure. This standardized system ensures that different individuals refer to the same compound using the same name, avoiding confusion and misinterpretations.
Examples of Correctly Named Compounds
- Sodium chloride(NaCl): A simple ionic compound composed of sodium cations (Na+) and chloride anions (Cl-).
- Methane(CH 4): A saturated hydrocarbon with a tetrahedral molecular structure.
- Ethanol(C 2H 5OH): An alcohol with a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom.
- Acetic acid(CH 3COOH): A carboxylic acid with a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to a methyl group (-CH 3).
- Glucose(C 6H 12O 6): A monosaccharide with a cyclic structure and multiple hydroxyl groups.
These examples illustrate the importance of precise naming in conveying the exact identity and structure of chemical compounds, enabling clear communication and avoiding misunderstandings.
Errors and Corrections
Chemical nomenclature is a systematic approach to naming chemical compounds. It is essential for clear and unambiguous communication in chemistry. However, errors in chemical nomenclature can occur due to various reasons, such as misunderstandings, misinterpretations, or lack of attention to detail.
Identifying and correcting these errors are crucial to ensure the accuracy and consistency of chemical information.
Common errors in chemical nomenclature include:
- Incorrect use of prefixes and suffixes to indicate the number of atoms or groups in a compound.
- Incorrect or missing parentheses or brackets to indicate groups or ions within a compound.
- Misspelling or incorrect capitalization of element symbols or group names.
- Incorrect use of Roman numerals to indicate oxidation states of metals.
- Inconsistent use of prefixes and suffixes for prefixes and suffixes for branched or complex structures.
To correct errors in chemical nomenclature, it is essential to refer to standard IUPAC guidelines and nomenclature rules. This involves carefully checking the spelling, grammar, and structure of the compound name. Additionally, using reliable resources such as chemical databases or reference books can help ensure the accuracy of the nomenclature.
Examples of Errors and Corrections
Consider the following examples of errors and corrections in chemical nomenclature:
- Error:Sodium chloride (I) Correction:Sodium chloride
- Error:Diphosphorus pentoxide Correction:Phosphorus pentoxide
- Error:Potassium permanganate(VII) Correction:Potassium permanganate
- Error:2-methylpropane Correction:2-methylpropane
- Error:1,2-dibromo-3-chloropropane Correction:1,2-dibromo-3-chloropropane
By understanding and correcting errors in chemical nomenclature, we can ensure the accuracy and reliability of chemical information, facilitate effective communication, and minimize confusion or misinterpretation.
Table of Compounds
The table below lists common compounds, their chemical formulas, IUPAC names, and common names.
Table of Compounds, Name the compounds. spelling counts
| Chemical Formula | Chemical Name | IUPAC Name | Common Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | Water | Dihydrogen monoxide | – |
| NaCl | Sodium chloride | Sodium chloride | Table salt |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide | Carbon dioxide | – |
| NH3 | Ammonia | Ammonia | – |
| CH4 | Methane | Methane | – |
General Inquiries: Name The Compounds. Spelling Counts
What are the key rules for naming inorganic compounds?
Inorganic compounds are typically named based on their constituent elements and their oxidation states, following specific rules and conventions.
How does accurate spelling impact the understanding of chemical formulas?
Correct spelling ensures that chemical formulas convey the precise composition and structure of compounds, enabling chemists to accurately interpret and utilize them.
Why is it important to distinguish between common and IUPAC names for compounds?
Common names may vary depending on the context or region, while IUPAC names provide a standardized and universally recognized nomenclature system, ensuring clarity and consistency in scientific communication.